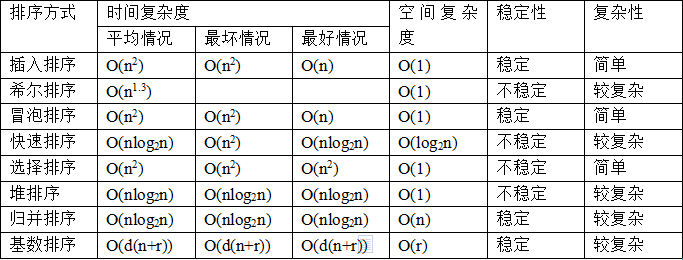
经典的排序算法自己手写一遍,并且归纳
快排
思想:把第一个数作为基准值,小于它的放左边,大于的放右边,之后再对左右两部分进行快排
代码:
private void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// 找寻基准数据的正确索引
int index = getIndex(arr, low, high);
// 进行迭代对index之前和之后的数组进行相同的操作使整个数组变成有序
quickSort(arr, low, index - 1);
quickSort(arr, index + 1, high);
}
}
private int getIndex(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
// 基准数据
int tmp = arr[low];
while (low < high) {
// 当队尾的元素大于等于基准数据时,向前挪动high指针
while (low < high && arr[high] >= tmp) {
high--;
}
// 如果队尾元素小于tmp了,需要将其赋值给low
arr[low] = arr[high];
// 当队首元素小于等于tmp时,向前挪动low指针
while (low < high && arr[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
// 当队首元素大于tmp时,需要将其赋值给high
arr[high] = arr[low];
}
// 跳出循环时low和high相等,此时的low或high就是tmp的正确索引位置
// 由原理部分可以很清楚的知道low位置的值并不是tmp,所以需要将tmp赋值给arr[low]
arr[low] = tmp;
return low; // 返回tmp的正确位置
}
归并排序
思想:先把数全部按中间切开分成两部分,一直分下去,之后再两两有序合并
代码:
public void mergeSort(int[] nums,int start,int end){
if(start==end) return;
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
mergeSort(nums,start,mid);
mergeSort(nums,mid+1,end);
mergeCore(nums,start,mid,end);
}
public void mergeCore(int[] nums,int start,int mid,int end){
int[] copy = new int[end-start+1];
int start1 = start;
int start2 = mid+1;
int copyIndex = 0;
while(start1<=mid&&start2<=end){
if(nums[start1]<nums[start2]){
copy[copyIndex++] = nums[start1++];
}else {
copy[copyIndex++] = nums[start2++];
}
}
while(start1<=mid){
copy[copyIndex++] = nums[start1++];
}
while (start2<=end){
copy[copyIndex++] = nums[start2++];
}
for (int i=0;i<end-start+1;i++){
nums[start+i]=copy[i];
}
}
冒泡排序
思想:依次比较,如果数大则往后沉,数组的最后面的部分是已经拍好的部分
代码:
public void bubbleSort(int[] nums){
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-i-1;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
swap(nums,j,j+1);
}
}
}
}
public void swap(int[] nums,int i,int j){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}